The stability of Syria holds significant importance for ensuring regional security
The region faces a growing threat of instability and disorder reminiscent of a contagious virus if nations do not actively participate in efforts to eliminate terrorist groups in Syria, experts warn.
Amid the ongoing ceasefire talks in Lebanon, attention has been diverted to a new development in Syria where remnants of terrorist factions, reportedly backed by Tel Aviv, have launched an assault on Aleppo. Notably, this offensive encountered minimal resistance initially and is now extending towards neighboring regions like Hama. However, in a significant counteraction over the past 24 hours, the Syrian military—bolstered by allies including Iran, Russia, and various Resistance groups—has dealt substantial setbacks to the Hay’at Tahrir al-Sham insurgents.
In a significant development in the ongoing fight against terrorism, reports have emerged regarding the alleged death of Abu Mohammad al-Julani, the leader of the Hayʼat Tahrir al-Sham militant organization. While confirmation is still pending, this marks a potentially pivotal moment in the efforts to combat extremist activities in the region.
A growing chorus of experts has expressed alarm over recent developments in northern and northwestern Syria, fearing a resurgence of the painful memories of the civil war. Concerns are mounting that the limited infrastructure remaining in the war-torn nation could succumb to attacks from Salafi-Takfiri extremist groups. This report examines the imperative of addressing the threat posed by Salafi-Takfiri terrorism and underscores the responsibilities of each component of the Resistance Axis in countering American militant influences.
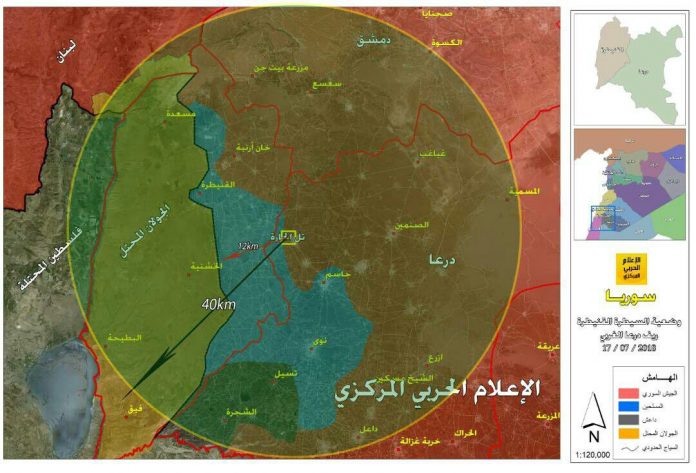
As global attention focuses on the actions of the Israeli regime in Gaza and Lebanon, militants based in Syria are reportedly seeking to undermine the Resistance Axis’s efforts to arm forces in Lebanon and the West Bank. The efforts by these militants to seize key communication routes, such as the “T-5” highway, or destabilize the Iraq-Syria border, suggest possible coordination between Tahrir al-Sham militants and the Israeli regime. While Israeli air forces target the transfer of arms to Lebanese fronts by striking advisory units, weapons depots, and communication routes, militants are positioned to act as ground forces and engage in potential clashes with Resistance groups.
In a recent operation by the coalition known as “Fath Al-Mobin,” terrorist groups have reportedly occupied the Iranian consulate in Aleppo and launched attacks on two Iranian consular facilities in Kafr Nabl and Khan Shaykhun, Syria. This development is attributed to a propaganda campaign allegedly orchestrated by the Mossad intelligence agency, which has reportedly depicted Iran and its allies as adversaries of the Islamic world. Such acts of aggression by Idlib-based militants are seen as a response to long-standing tensions, stemming from their perceived defeat and suppression by the Axis of Resistance across various regions in Syria throughout the years of the civil conflict.
Analysis: Examining the Potential Connections Between the Ukraine and Syria Conflicts
There is a growing discourse among geopolitical analysts regarding the possible interlinkages between the ongoing conflicts in Ukraine and Syria. Both regions have been focal points of international tension and have drawn significant involvement from global powers, creating a complex web of diplomatic and military interactions. Observers note that while the contexts and origins of the crises differ, the involvement of key stakeholders such as Russia and the United States may suggest underlying strategic parallels or coordinated policies. Understanding these potential connections is critical for comprehensively addressing the impacts on global security and international relations.
The Kremlin, under the influence of Neo-Eurasianist thinkers, recognizes Syria’s crucial role in the geopolitical rivalry with Western powers. Following the disintegration of the Eastern Bloc, NATO, spearheaded by the United States, aimed to extend its influence into Russia’s immediate vicinity, a region often referred to as the “Near Abroad.” The continuing conflict in Ukraine and the persistent instability in Georgia illustrate the enduring support for this strategy among Western leaders. In counteraction, President Vladimir Putin opted to engage in a geopolitical contest with the United States.
The escalating geostrategic rivalry between Moscow and NATO along the Crimea-Donbas region has prompted militant factions to perceive the potential weakening of Russia’s military presence in Syria as an opportune moment to embark on fresh battlefield endeavors, aided by intelligence support from their allies. Tahrir al-Sham militants view their foothold in Aleppo as a significant gain; however, the reported demise of al-Julani at the hands of a Sukhoi-34 underscores Moscow’s steadfast commitment to safeguarding Damascus. Russia is aware that Turkey and Israel have aligned with the United States amid the great power competition and are indifferent to Moscow’s interests over the long term. By supporting Syria, Moscow sends a clear signal to Western nations that it has no intention of ceding influence to NATO in the strategic developments occurring around the Mediterranean Sea.
**Terrorism is Indiscriminate Regarding Allies and Adversaries**
In the early days of internal strife in Syria, experts noted significant connections between certain Islamist factions and Turkey, leading them to identify Ankara as a key supporter of terrorist groups based in Idlib. Up until 2016, Turkey’s primary objective in involving itself in Syrian affairs was the ousting of Bashar al-Assad’s regime. However, following a shift in U.S. leadership, Turkey redirected its focus, leveraging terrorist groups to counter Kurdish forces. The Turkish military has conducted four operations along the country’s northern and northwestern borders, citing the emergence of any Kurdish political entity along Turkey’s southern borders as a security threat. Currently, Turkey justifies its involvement by invoking the implementation of UN Security Council Resolution 2254, the swift repatriation of Syrian refugees, and the facilitation of free elections in Syria.
According to confessions obtained from detained militants, Turkey has been accused of offering various forms of military, financial, and intelligence support to the Syrian opposition. In March 2020, Ankara reportedly pledged to Tehran and Moscow that should Damascus halt its anti-terror operations, Turkey would work to contain extremist elements in Idlib and promote the rise of a moderate faction in the region. However, developments as of November 2024 appear to contradict this assurance. Questions are being raised toward Ankara’s leadership regarding the possibility of redirecting military resources to Lebanon or the occupied Golan Heights to assist Resistance forces in the Palestinian cause. Critics argue that confronting Israel requires more than public statements or political rhetoric but necessitates tangible actions on the ground.
**Summary**
The recent lack of adequate military presence along the borders of Idlib province, coupled with shifts in Damascus’s alliance dynamics amidst ongoing conflicts in Gaza, Lebanon, and Ukraine, has allowed Tahrir al-Sham militants to seize the opportunity and launch attacks on Aleppo’s industrial region. This underscores the urgent need to address the Syrian crisis, as the involvement of external powers has rendered West Asia vulnerable to turmoil. Should regional nations fail to effectively counter the terrorist factions entrenched in Syria, the resultant insecurity and disorder have the potential to rapidly proliferate across the region. Moreover, Turkey must remain cognizant of the fact that an escalation of instability in northern Syria could pose significant threats to its own border security.